Section: New Results
Parallel adaptively restrained particle simulations
Participants : Krishna Kant Singh, Stephane Redon.
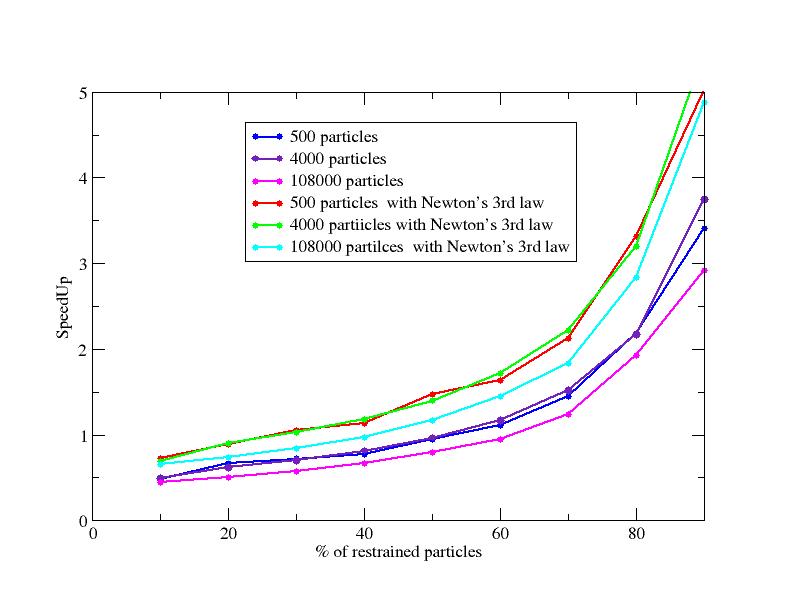
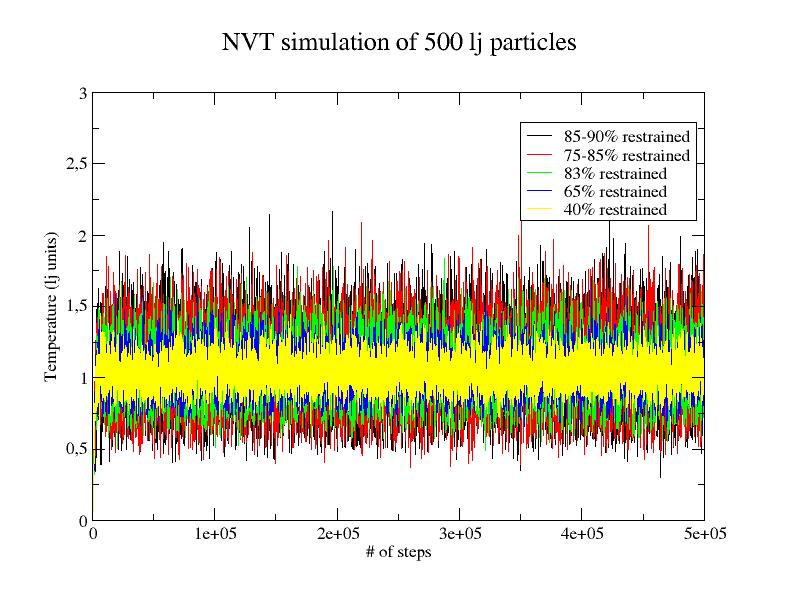
We have continued our work on the development of parallel adaptively restrained particle simulations. We developed new algorithms for neighbor list and incremental force updates. These algorithms have advantages over the state-of-the-art methods for simulating a system using Adaptively Restrained Molecular Dynamics (ARMD). We have simulated systems with different number (500, 4000 and 108000) of LJ particles using adaptively restrained integrator and Lennard-Jones potential in NVE (constant number of particles, Volume and Energy) and NVT ensemble (constant number of particles, Volume and Temperature). All the particles were placed in an orthogonal box. We used periodic periodic boundary conditions with 8.5 angstrom cut-off for the Lennard-Jones potential. The system was simulated using 2 femtoseconds. We compared the LAMMPS algorithm to adaptive algorithm while using adaptively restrained integrator. Our results show that a significant speed-up can be achieved if more than of the particles are restrained (Figure 4 ). Figure 5 shows that ARMD in NVT ensemble preserves the average temperature of the system (irrespective of number of restrained particles).